Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)¶
Overview
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is widely used in the cybersecurity industry as a standard method for assessing the "severity" of security vulnerabilities.
In this section, we analyze CVE CVSS values to understand opportunities for prioritization based on these values:
- CVSS Severity Rating
- CVSS Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability Impacts
CVSS Severity Rating Scale¶
Quote
"The use of these qualitative severity ratings is optional, and there is no requirement to include them when publishing CVSS scores. They are intended to help organizations properly assess and prioritize their vulnerability management processes."

https://www.first.org/cvss/v3.1/specification-document#Qualitative-Severity-Rating-Scale
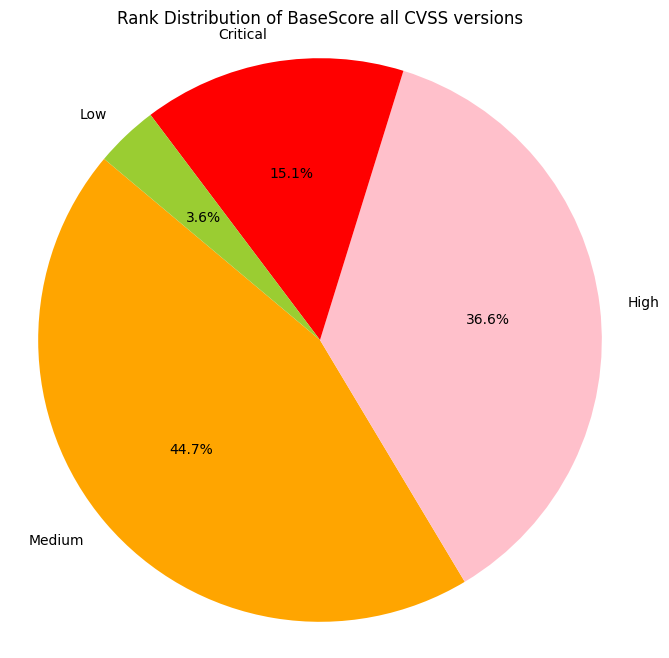

Observations
- ~~15% of CVEs are ranked Critical (9+)
- ~~40% of CVEs are ranked High (7.0 - 8.9)
- ~~60% of CVSS v3 CVEs are ranked Critical or High (7+)
- >96% of CVEs are ranked Medium or higher (4+)
Don't use CVSS Base Scores alone to assess risk¶
Don't use CVSS Base Scores alone to assess risk.
Many organizations use CVSS Base Scores alone to assess risk despite repeated guidance against this.
A Critical or High CVSS Severity is not the same as a Critical or High Risk.
There's a ~10x difference in counts of CVEs for these 2 groups:
- >50% of CVEs are ranked Critical or High CVSS rating (CVSS score 7+)
- ~~5% of CVEs are exploited in the wild
Quote
CVSS Base (CVSS-B) scores are designed to measure the severity of a vulnerability and should not be used alone to assess risk.
https://www.first.org/cvss/v4.0/user-guide#CVSS-Base-Score-CVSS-B-Measures-Severity-not-Risk
CVSS Requirements for Regulated Environments¶
Some Regulated Environments requirements appear to conflict with this guidance 🤔
PCI¶
Quote
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is an information security standard used to handle credit cards from major card brands. The standard is administered by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council, and its use is mandated by the card brands. It was created to better control cardholder data and reduce credit card fraud. Validation of compliance is performed annually or quarterly with a method suited to the volume of transactions
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Payment_Card_Industry_Data_Security_Standard
Quote
PCI DSS 4.0 11.3.2.1 “External vulnerability scans are performed after any significant change as follows: Vulnerabilities that are scored 4.0 or higher by the CVSS are resolved.”
https://docs-prv.pcisecuritystandards.org/PCI%20DSS/Standard/PCI-DSS-v4_0.pdf
FedRAMP¶
Quote
The Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) is a United States federal government-wide compliance program that provides a standardized approach to security assessment, authorization, and continuous monitoring for cloud products and services https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FedRAMP
Quote
3.0 Scanning Requirements
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) Risk Scoring: For any vulnerability with a CVSSv3 base score assigned in the latest version of the NVD, the CVSSv3 base score must be used as the original risk rating. If no CVSSv3 score is available, a CVSSv2 base score is acceptable where available. If no CVSS score is available, the native scanner base risk score can be used.
https://www.fedramp.gov/assets/resources/documents/CSP_Vulnerability_Scanning_Requirements.pdf
CVSS Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability Impacts¶
Quote
- The Confidentiality and Integrity metrics refer to impacts that affect the data used by the service. For example, web content that has been maliciously altered, or system files that have been stolen.
- The Availability impact metric refers to the operation of the service. That is, the Availability metric speaks to the performance and operation of the service itself – not the availability of the data.”
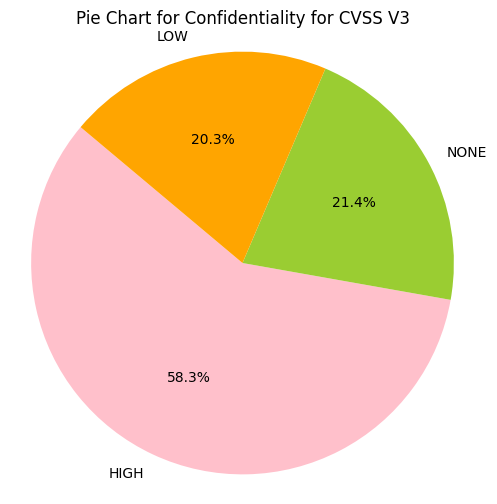

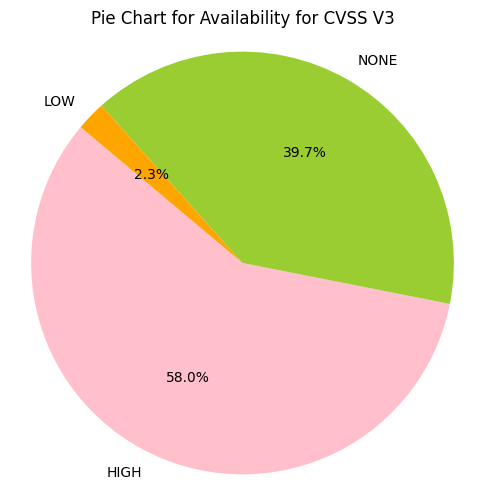
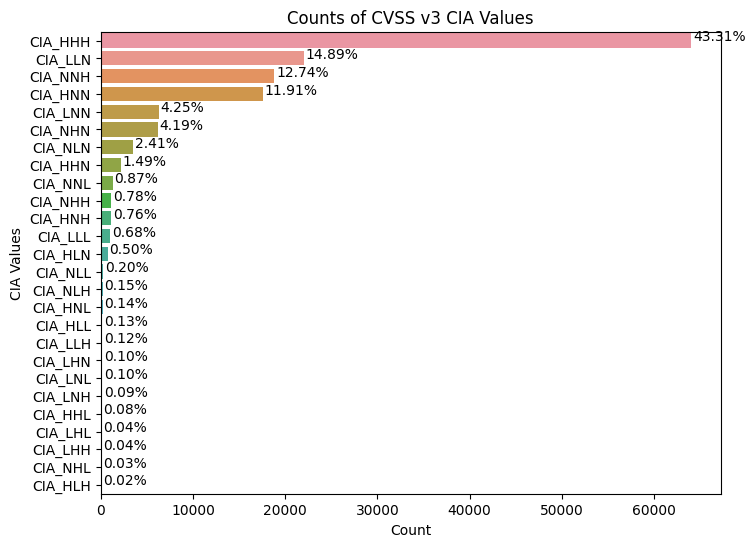
e.g. CIA_HHH means that Confidentiality Impact is HIGH, Integrity Impact is HIGH, Availability Impact is HIGH
Observations
- Greater than 50% of CVE Confidentiality Impact, Integrity Impact, Availability Impact values are HIGH.
- There are 27 (3x3x3) possible combinations of Confidentiality Impact,
Integrity Impact, Availability Impact and possible HIGH, LOW, NONE
values
- ~43% of CVSS v3 CVEs have Confidentiality Impact, Integrity Impact, Availability Impact value of HIGH
- The top 4 account for 83% of CVSS v3 CVEs
- So there isn't much granularity for prioritization based on
- CVSS Base Score or Rating
- CVSS Impact values
CVSS Exploit Maturity¶
In addition to the CVSS Base Metrics which are commonly used, CVSS supports other Metrics, including Threat Metrics.
Quote
It is the responsibility of the CVSS consumer to populate the values of Exploit Maturity (E) based on information regarding the availability of exploitation code/processes and the state of exploitation techniques. This information will be referred to as “threat intelligence” throughout this document.
Operational Recommendation: Threat intelligence sources that provide Exploit Maturity information for all vulnerabilities should be preferred over those with only partial coverage. Also, it is recommended to use multiple sources of threat intelligence as many are not comprehensive. This information should be updated as frequently as possible and its application to CVSS assessment should be automated.
https://www.first.org/cvss/v4.0/specification-document#Threat-Metrics
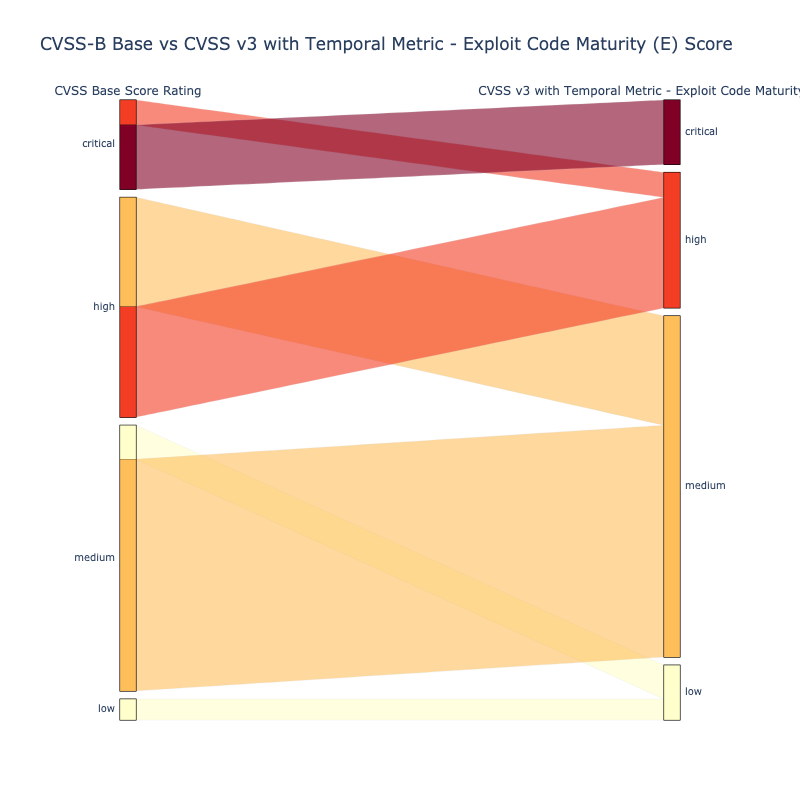
CVSS v3.1¶
The "Temporal Metrics - Exploit Code Maturity (E)" causes the CVSS v3.1 Score to vary slightly.
- High (H): 9.8
- Functional (F): 9.6
- Proof-Of-Concept (P): 9.3
- Unproven (U): 9.0
- Not Defined (X): 9.8 results in the same score as High (H): 9.8
An example project that enriches NVD CVSS scores to include Temporal & Threat Metrics
"Enriching the NVD CVSS scores to include Temporal & Threat Metrics" is an example project where the CVSS Exploit Code Maturity/Exploitability (E) Temporal Metric is continuously updated.
- Fetches EPSS scores every morning
- Fetches CVSS scores from NVD if there are new EPSS scores.
- Calculates the Exploit Code Maturity/Exploitability (E) Metric when new data is found.
- Provides a resulting CVSS-BT score for each CVE
It uses an EPSS threshold of 36% as the threshold for High for Exploit Code Maturity/Exploitability (E).
Count of CVEs at or above CVSS Base Score and CVSS Base and Threat Score¶
The data from "Enriching the NVD CVSS scores to include Temporal & Threat Metrics" is used here.

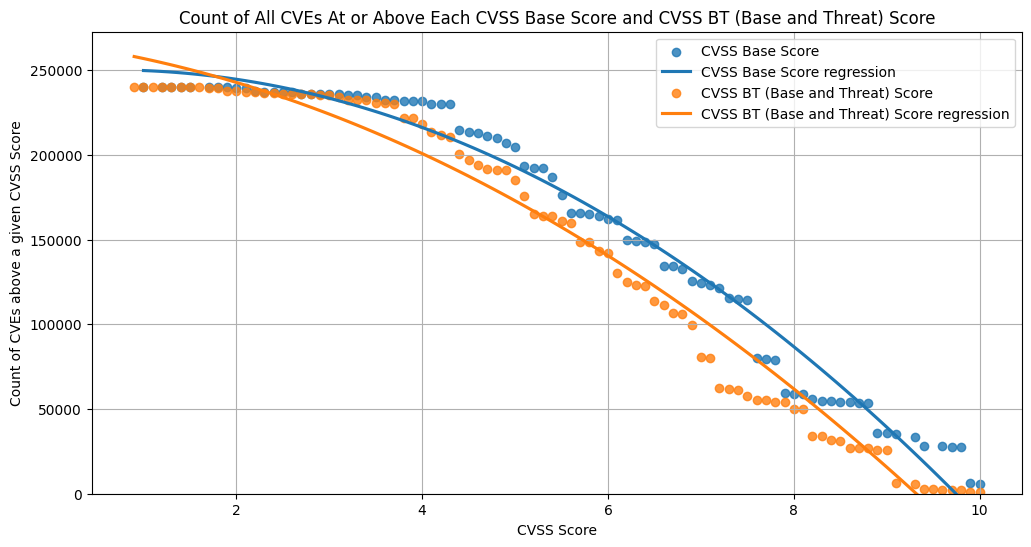
The continuous line is a polynomial regression of order 2.

Observations
- For CVSS Base and Threat
- there's a lot less CVEs above a score of ~9 (relative to CVSS Base)
- ~~35% of CVEs are High or Critical (versus ~~55% for CVSS Base)
CVSS v4.0¶
The Threat Metrics - Exploit Maturity (E) value causes the CVSS v4.0 Score to vary slightly
- Unreported: 8.1: High
- POC (P): 8.9: High
- Attacked (A): 9.3: Critical.
- Not Defined (X) results in the same score as Attacked (A)
Quote
The Threat Metric Group adjusts the “reasonable worst case” Base score by using threat intelligence to reduce the CVSS-BTE score, addressing concerns that many CVSS (Base) scores are too high.
The convenience of a single CVSS score comes with the cost of not being able to understand or differentiate between the risk factors from the score, and not being able to prioritize effectively using the score.
Takeaways
- Don't use CVSS Base (CVSS-B) scores alone to assess risk - you will waste a LOT of time/effort/$ if you do!
- CVSS Base scores and ratings don't allow for useful prioritization (because there's too many CVEs at the high end)
- CVSS Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability Impacts don't allow for useful prioritization (because there's too many CVEs with HIGH or CRITICAL values)
- CVSS Threat Metrics - Exploit Maturity (CVSS-BT) values don't allow for useful prioritization (because there's too many CVEs with HIGH or CRITICAL values) - but are still useful as the number of CVEs with HIGH or CRITICAL ratings is reduced.
- The convenience of a single CVSS score comes with the cost of not being able to understand or differentiate between the risk factors from the score, and not being able to prioritize effectively.