Yahoo¶
Overview
Yahoo is a large Media, Social, Internet enterprise.
It has a mature DevOps and data analysis capability.
Simplified representative views are presented below.
The content is based on what was presented at BSidesDublin 2023:

3 R's to address Risk Effectively
3 R's to address Risk Effectively¶
Rather than playing whack-a-mole with vulnerabilities, the following 3 independent steps are applied to focus on what needs to be fixed first (where each step on its own gives a very significant reduction in CVEs to fix):
- Root Cause
- Do some initial easy Exploratory Data Analysis to understand the
root causes of CVEs in the DevOps pipeline i.e. find the source
of the moles and address them.
- One Programming Language in particular accounted for a very
significant proportion of CVEs
- This was due to the Open Source dependencies for this programming language not being up to date
- By updating dependencies (automatically), the number of CVEs reduced very significantly over time!
- One Programming Language in particular accounted for a very
significant proportion of CVEs
- Addressing the root cause avoids playing whack-a-mole by eliminating the source of the moles
- Do some initial easy Exploratory Data Analysis to understand the
root causes of CVEs in the DevOps pipeline i.e. find the source
of the moles and address them.
- Reachability
- Some (SCA (Software Composition Analysis) and image scan) tools
support reachability analysis that indicate if a vulnerability
in the vulnerable dependency is actually called by the App code
or not
- in general, a significant number of CVEs reported by SCA, image scanners are not reachable.
- There are also tools that check Network reachability of vulnerabilities, and some validate exploitability.
- Some (SCA (Software Composition Analysis) and image scan) tools
support reachability analysis that indicate if a vulnerability
in the vulnerable dependency is actually called by the App code
or not
- Risk Based Prioritization
- As seen throughout this guide, focusing on CVEs that are, or are likely to be, exploited, gives a very significant reduction in CVEs to remediate and associated effort!
Risk Based Prioritization¶
https://github.com/theparanoids/PrioritizedRiskRemediation gives the background and detail to this section.
A Risk Remediation Taxonomy is defined here to support Risk Based Prioritization of CVEs:
- the constituent components of risk and remediation for a CVE
- the associated data sources for these components
A Risk-based Decision Tree is defined with
- inputs for the Decision Tree Decision Nodes
- output Decisions
The Risk Remediation Taxonomy and Decision Tree are part of a conference presentation by Yahoo Chris Madden: https://www.bsidesdub.ie/ May 27 2023.
- See the slide deck and the recording.
CVEs CVSS scores, counts of CVEs, EPSS scores¶
The counts of a specific CVE in an organization are a relevant part of Risk Based Prioritization.
The data from different tools across the DevOps pipeline shows there are Paretos i.e. a relatively small number of unique CVEs account for a large number of overall CVEs per https://youtu.be/oMZN810xfck?t=896.
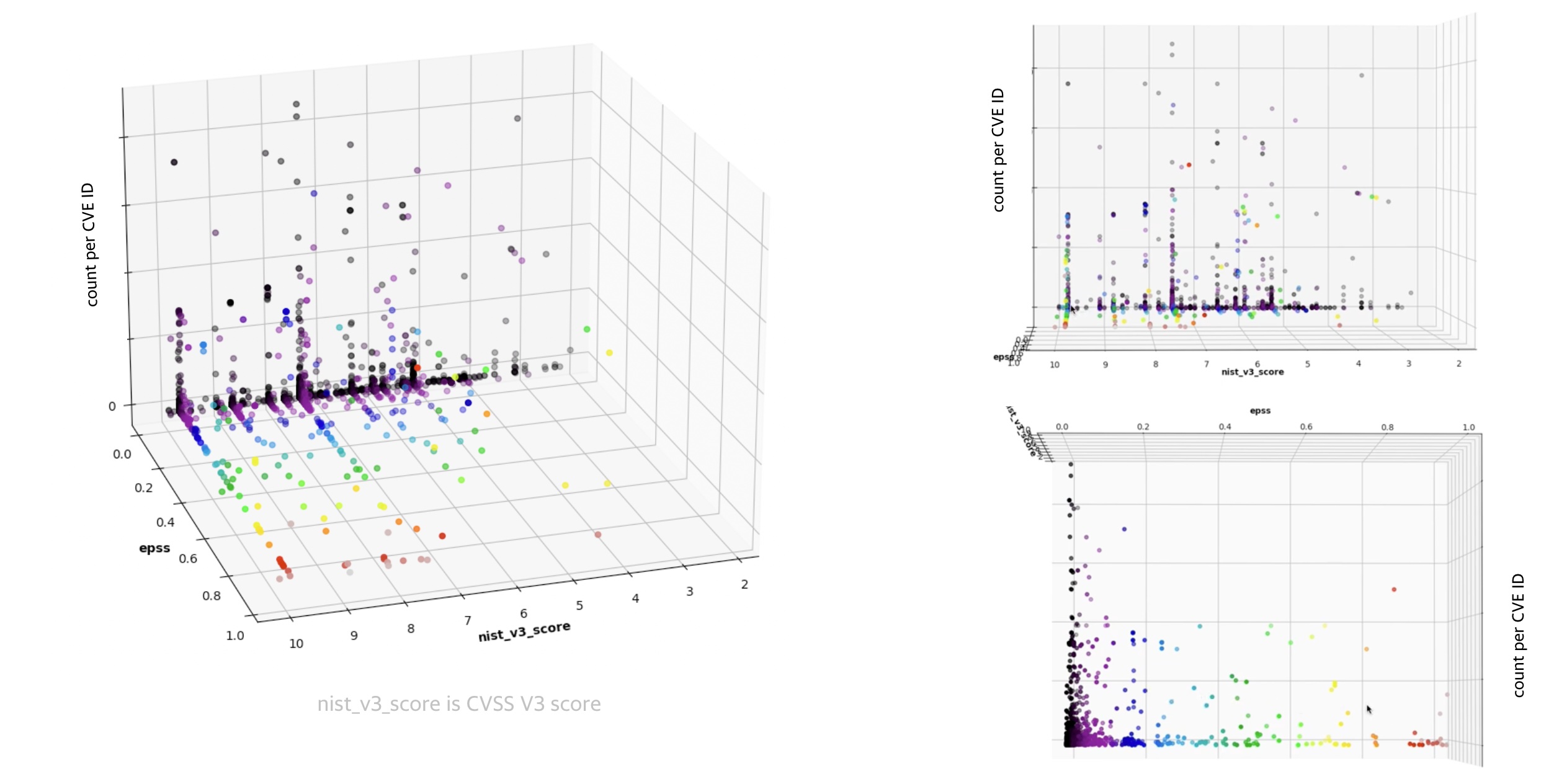
The plots are based on real data (the pattern is the same whether 1 or several tools in the DevOps pipeline are viewed, or an aggregate of CVEs across those tools).
Decision Trees and Multiple Data Sources to get more Targeted Prioritization¶
The Decision Tree From Scratch section gives a simplified view of the Decision Tree used.
Using the same real data, using CVSS Base Parameters (not CVSS Score), and combining EPSS with CISA KEV and other industry and internal threat intelligence using Decision Trees based on CISA SSVC.
The Decision Tree is similar to the "Decision Tree from Scratch" example code provided but
- additionally uses commercial CTI for Exploitation
- uses other sources of Impact (because CVSS Base Score Impact Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability do not offer enough granularity per CVSS ratings.)
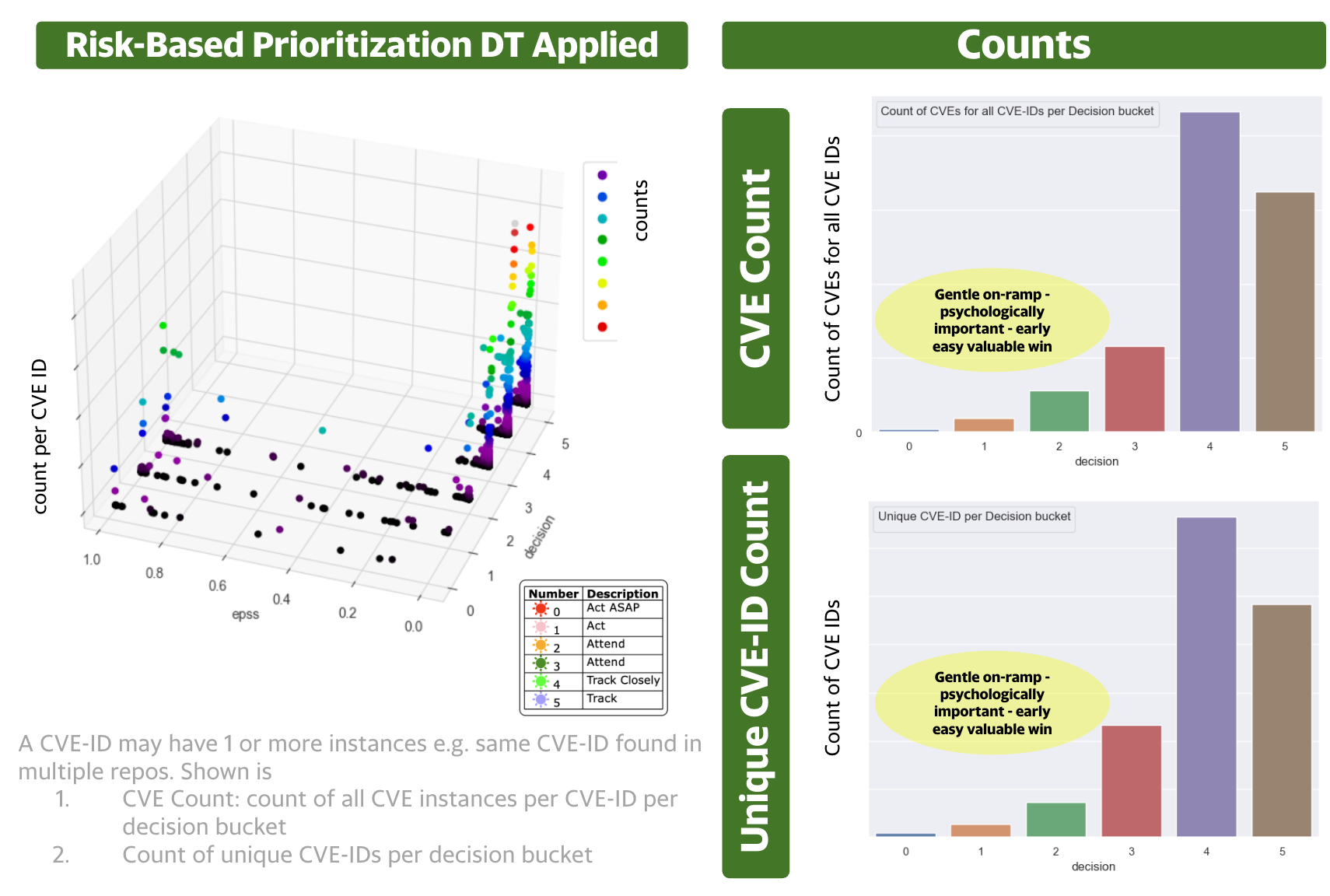
Observations
- There's a concentration of CVEs in the lower EPSS range below 0.1.
- The CVSS score distribution is typical in industry
- The EPSS score (temporal) can be used in conjunction with the static decisions to prioritize across a decision band.